We’ve all been there. You’re trying to upload a video, send a large file, or even just post a photo on social media, and it’s taking forever. Your upload speed seems to be crawling at a snail’s pace. But why is this happening? And more importantly, how can you fix it? In this post, we’ll explore the reasons behind slow upload speeds and provide step-by-step instructions to troubleshoot and resolve these issues.

Upload Speed vs Download Speed – What Is The Difference
Upload speed and download speed are two sides of the same coin, both crucial for a smooth internet experience. Download speed refers to how quickly data can be transferred across the internet from a website or server to your device, like when you’re streaming a movie or downloading a file.
On the other hand, upload speed is how quickly data can be sent from your device to the internet, like when you’re posting a photo on Instagram or sending an email with a large attachment. While most of us notice download speeds more in our daily internet use, upload speeds are equally important, especially in today’s work-from-home and content creation era. If you find you are suffering slow download speeds on your PC, chances are your upload speeds are suffering too!
Common Reasons For Slow Upload Speeds
There are several reasons why your upload speed might be slower than you’d like. Some reasons might be easy or at least within your reach to resolve, while others may signal equipment reaching end of life. Then there are those reasons that are out with your control and will need a little patience. Here are some of the most common:
Older or Outdated Equipment:
If your router and/or modem are getting old, they may not have the capacity for higher upload speeds. This was a common problem when many connections started to change over from old copper wire broadband lines to fibre optic. The new technology required new routers that could cope with the jump in potential capacity.
If you are moving from an old property with copper wires, into a new property that already has fibre optic supply, as another example, you might find that your old router can’t do your service justice.
It might also be that your computer is getting old, or that there are lots of processes running that are causing your laptop to run slow, and this is impacting the amount of resources your machine has to deal with data transfer.
Poor Router Placement:
The signal from and to a WiFi router can be affected by physical objects between the router and your computer, or any other WiFi device. Walls, furniture and even pipes in walls can all reduce the optimal range of your WiFi signal, and impact the speed that you receive if your computer is in another room, far from the router. Other electronic devices can also cause interference impacting the signal you receive. More interference can cause slower internet speeds and unreliable connections.
Network Congestion:
If too many devices are connected to your network and trying to upload at the same time, your upload speeds will slow down. It won’t just impact upload speeds, but download speeds too. Data travelling in either direction can be impacted by network congestion as the bandwidth is limited and data both back and forth use up your capacity.
So if you have 2 or 3 devices all streaming Netflix is separate rooms for example, and you are trying to upload files to a website, like photos to Instagram for example, this can have an impact on your upload speed.
ISP Limitations:
Your internet provider might not be giving you the maximum speed listed on your plan. This might be due to limitations with the line coming into your property from the exchange, or the distance of your property to your nearest exchange. Or, it may be that you are on a capped plan, say a 10MB broadband plan that has limits on your speeds up and downstream. The other reason may be for a fair usage policy violation.
Malware:
Malware can disrupt your normal computer activities and slow down your upload speed. While unlikely, it’s always good to have reliable antivirus and check for malware and spyware regularly!
How To Fix Slow Upload Speeds – Troubleshooting & Fixes
Check Your Internet Speed:
The first thing to check, is that you are getting the speeds you are paying for. Now, upload speeds are always less than download speeds so be aware of that. The service is designed that way, because people use more resources downloading than uploading.
When you are uploading from a computer, it is usually a file much smaller than one you might want to download from the web. For example, uploading images to Insta, or a video to YouTube, is far less demanding than downloading a new Xbox game. So ISPs design the net to give download traffic the biggest slice of the highway.
Your ISP should advise you clearly on what speeds you can expect for your line, and the package you are paying for. You can check if you are getting this service by running a speed test, with a tool like Fast or Speedtest By Ookla. Simply:
- Browse to your chosen Speedtest app in your web browser.
- Click on the ‘Go‘ or ‘Start‘ button.
- Wait for the test to complete and review your upload speed.
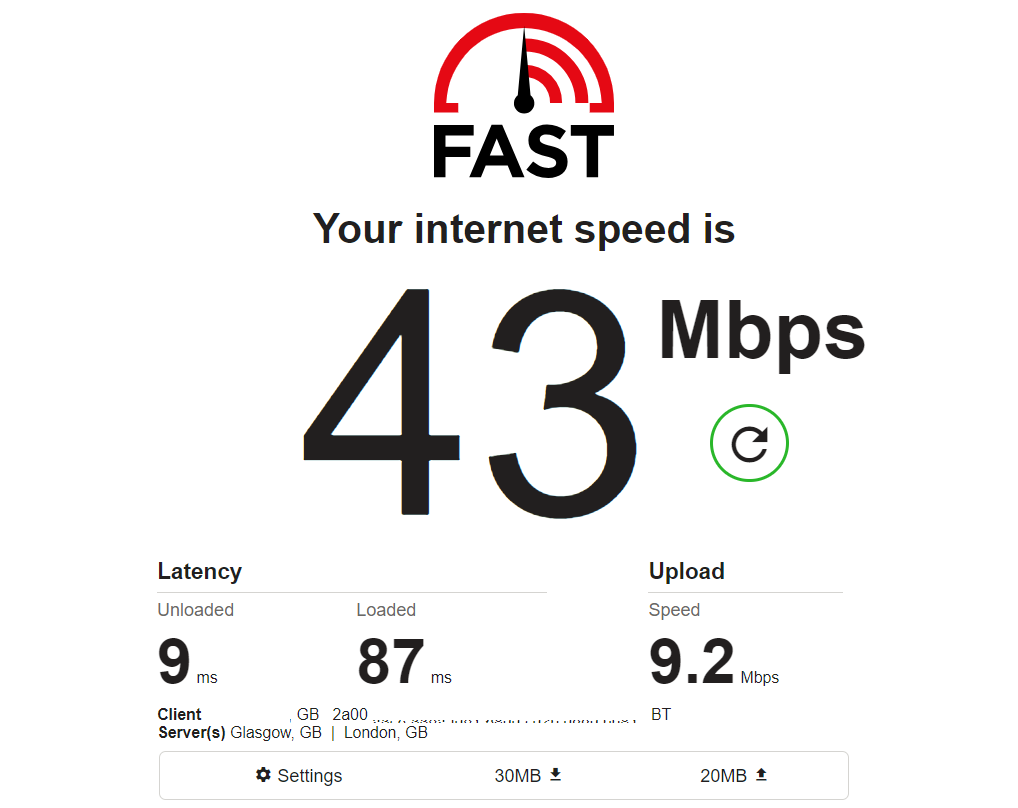
You can see in the test above, the downstream speeds are around 43 Mbps, and upload speeds are around 9.2 Mbps. For me, this is a normal result and it does illustrate the difference you can expect between upload and download.
Now, if the speed result showed an abnormal result that didn’t match the package I am paying for, say the download speeds were around 1 Mbps, that would suggest to me that there is a problem that needed further testing.
In that scenario, I would probably, for this example, move to the ‘router placement‘ or ‘Ethernet‘ steps that I go through below.
Limit Your Uploads At Busy Times:
If you are trying to upload files on a busy network, while others in your house are gaming or streaming, this can slow down your uploads considerably. Especially on a capped package. If you must upload at peak times, try to reduce the demand to one file at a time.
If possible, schedule large uploads for times when your network is less busy, like late at night or early in the morning. The more devices that are streaming, gaming or downloading, the more demand on your service. Pick a quieter time and you maximise your upload speed potential.
Cable Connections & Contention Ratio
Also, if you are no an older DSL broadband connection, it’s not just people on your home network that can slow your speeds down. Similarly to cable broadband, these services have a capacity that is not only impacted by users in your home, but other houses using the same network coming from your local exchange.
This is referred to as a contention ratio, which basically means the ‘ratio of the potential maximum demand to the actual bandwidth‘. If you are getting a contention ratio of 10:1 from your local exchange, then your service will be much more impacted at peak times than someone with a contention ratio of say, 2:1. This can be an issue with old copper wire services coming from an exchange.
If you have a high contention ratio, you may wish to look at upgrading to fibre optic if possible, or a high speed alternative to Cable or DSL.
Use an Ethernet Connection:
One important test you can try, is to see if using an Ethernet connection improves your download speeds. This can tell you a number of things to direct your troubleshooting further in the right direction. If it improves your speeds, it can also be enough to get you through whatever it is you are trying to upload at this time.

To do this:
- Connect an Ethernet cable to the LAN port on your router.
- Connect the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on your computer.
- You might need to move your computer or laptop closer to your router to do this.
- Disconnect from your Wi-Fi network to ensure your computer is using the wired connection.
- At this stage you can either run a speed test again, or simply try to upload your files and see if it makes a difference.
If you notice no difference, this might suggest either a problem with the router, or with the incoming internet supply.
If other devices are working fine with normal speeds, then this might suggest an issue with your PC, but if they are also suffering, this would add evidence to the likelihood of a line or router problem.
Upgrade Your Internet Plan:
If you are on a budget or a capped plan, with strict speed and data transfer allowances, this could result in throttling or limitations to your service if you exceed the cap. If you are transferring lots of data at peak times too, this may trigger a fair usage violation with your ISP.
These are not common on high speed fibre packages, but there are still some packages that enforces these on standard DHL, and Cable broadband packages. Some satellite providers too also have fair usage policies to try and ensure their networks don’t get choked.
Your problem might also be, that you are simply using up your allowances too quickly and need a bigger package to handle all the date you are transferring back and forth.
If you think this is the case:
- Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to discuss your current plan.
- Ask about higher-tier plans that offer faster upload speeds.
- Upgrade your plan and/or router if necessary.
Run an Antivirus Check:
Malware, Viruses or Spyware can be a real bugger if they find their way onto your machine. They can be very resource heavy, putting a lot of demand on your CPU and slowing everything down, including your upload speeds. They will often run in the background, spying and transferring data back and forth and the only indication that you get is that everything is slow and perhaps your fan sounds like it is going to take off.
To prevent malware and spyware you should do this regularly:
- Open your antivirus software. Windows Defender is good, but having a separate, dedicated and comprehensive antivirus suite is always recommended.
- Select the option to run a full system scan.
- Follow the software’s instructions to quarantine or remove any threats it finds.
- You might want to look at adding tools like Spybot to your anti threat arsenal too. They can complement the work your antivirus does and often pick things up that others don’t.
Turn Off Your VPN:
If you are using a VPN, this might be impacting your upload speeds. A VPN works by essentially encrypting your data (IP, location details etc), routing your connection through a secure server in a completely different location allowing you to browse the internet anonymously.
While these are great for protecting your information, there can on occasion be an issue with the server you are masking your IP through, or a conflict between your ISP and the VPN depending on it’s type and level (device or network). Some routers actually have VPNs within them!
If you notice, for example, that your PC is having data transfer issues, and uploading is taking forever, but your other devices are not having the same problem. While at the same time your PC is the only device to be using a VPN, then this might signal that the VPN is the issue.
It’s east to test this:
- Open your VPN application on your applicable device.
- Simply disconnect from the VPN server.
- Close the VPN application to ensure it’s not running in the background.
Optimize Your Router Placement:
If your PC or laptop is far away from your router this could be impacting your upload speeds. Are your speeds ok on any other devices that are close to the router? If so, that would backup this theory.
WiFi speeds reduce in potency the further you are from a router. While documentation may say the range is up to 40 feet for example, if there are walls, furniture, pipes and other devices in the way, that range can be reduced significantly.
Now I know it’s not just the device having upload speed issues that you are probably connecting to in your home, but this is exactly why finding an optimal place to house your router in your home is important. So that all devices in all rooms have a reasonable signal.
So, tips for optimal placement include:
- For your ‘big ticket’ devices, particularly those you work on or that have a heavy demand, try to ensure they have line-of-sight to the router to reduce the risk of interference from obstacles and other devices.
- Where possible, place your router in a central location in your home.
- Keep the router elevated and free from physical obstructions.
- Adjust the antennas to point upwards for the best signal distribution.
If you are restricted to where you can place the router in your home, you might want to invest in a WiFi booster to plug in between your router and the problem signal area in your home. These can amplify your signal and extend the range to improve low signal areas. A better signal would mean more stable data transfer speeds.
Update Your Router Firmware:
If you suspect the router has developed a fault, you might want to consider updating the firmware. When all your devices are having speed issues, your ISP has confirmed there is no fault on the line, and your devices work fine on another router, this might indicate such an issue.
Before considering the firmware as the issue, you should also have tried resetting and rebooting your router, to offer it a change to boot fresh and remove any little software glitches or niggles that might have occurred.
Now, updating the firmware often has a different process from router to router, depending on the manufacturer and the device. One common thing you will need though, is access to the admin console for your router. The details for this (IP address and admin password) are usually written on your router, or with the documentation that came with it.
To update the firmware for your router:
- Visit your router manufacturer’s website and find the latest firmware update for your specific router model.
- Download the firmware update.
- Access your router’s settings by typing its IP address into your web browser.
- Find the firmware update option and upload the file you downloaded.
- Follow the prompts to install the update.
- If your router doesn’t have a firmware update option, you may wish to select ‘factory reset’ or ‘restore’ and the firmware should reinstall following that process.
Replace Your Router:
If all other troubleshooting has failed, you might want to consider it being time to replace your router.
If your devices are all fine and the line is confirmed as faultless, then it could just be that your router is approaching end of life.
Other reasons you might need to replace the router include:
- If it is an old router and you have moved into a new property with a high speed service that the router can’t cope with.
- The router can only connect to a limited number of devices and you are using more than that limit
- The range is poor
- It only works on 2.4GHz and some of your devices require 5 GHz.
Your ISP should provide you with a suitable router to handle the service that they provide you. But if you have been with them for a long time and your router has just reached a legacy age you should contact them to replace the hardware with a modern router.
If you want to chose your own router, then research and purchase a new router that supports higher upload speeds, and all your devices.
- Disconnect your old router and set up the new one according to its instruction manual.
- Connect your devices to the new router’s network SSID, with the new network password.
- You will need to update the network and login credentials on each of the devices you want to connect to the new router.
Contact Your ISP:
If you’ve tried everything and your upload speed is still slow, contact your ISP. It could be that there is a problem with your line. Not enough to cut out your service, but enough to limit the service you are receiving. This sometimes happens after floods, where they cause problems in local exchanges and cabinets. Or where old copper wires start to fail if they have not been replaced for ‘full fibre’ yet.
Discuss the issue you are having with them and ask for further assistance or a technician visit. Make sure you advise them of all the troubleshooting steps you have already taken before calling.
Remember, always proceed with caution when making changes to your network or devices. If you’re unsure about any step, it’s best to consult with a professional or your ISP.
Are you having slow WiFi speed issues, and are these effecting different devices in your home? You might want to check out some of my guides on this:



